
Decoding and sending 433MHz RF codes with Arduino Electronics Infoline Electronics Infoline
In order to decode that bit pattern, you have to know, or have a very good guess for what data are being transmitted. Here is a general approach for unknown protocols, showing how to decode the signals from 433 MHz weather sensors: Reverse Engineer Wireless Temperature / Humidity / Rain Sensors — Part 1 « RAYSHOBBY.NET.

ArduinoBasics 433MHz RF Tutorial 2 YouTube
Hold your remote near your receiver module and press a button. The Arduino should decode the signal and print the results in the serial monitor. This is what I got for my remote-controlled mains switch when I press the button to turn channel 5 on: Decimal: 3932352 (24Bit) Binary: 001111000000000011000000. Tri-State: 011000001000.

How To Decode 433Mhz Low Power Devices Using RTL433 And A RTLSDR Receiver YouTube
You need to decode the signals that your remote control sends, so that the Arduino or ESP8266 can reproduce those signals and ultimately control the outlets. The library comes with several sketch examples. Within the Arduino IDE software, you need to go to File > Examples > RC_Switch > ReceiveDemo_Advanced. This next sketch opens:
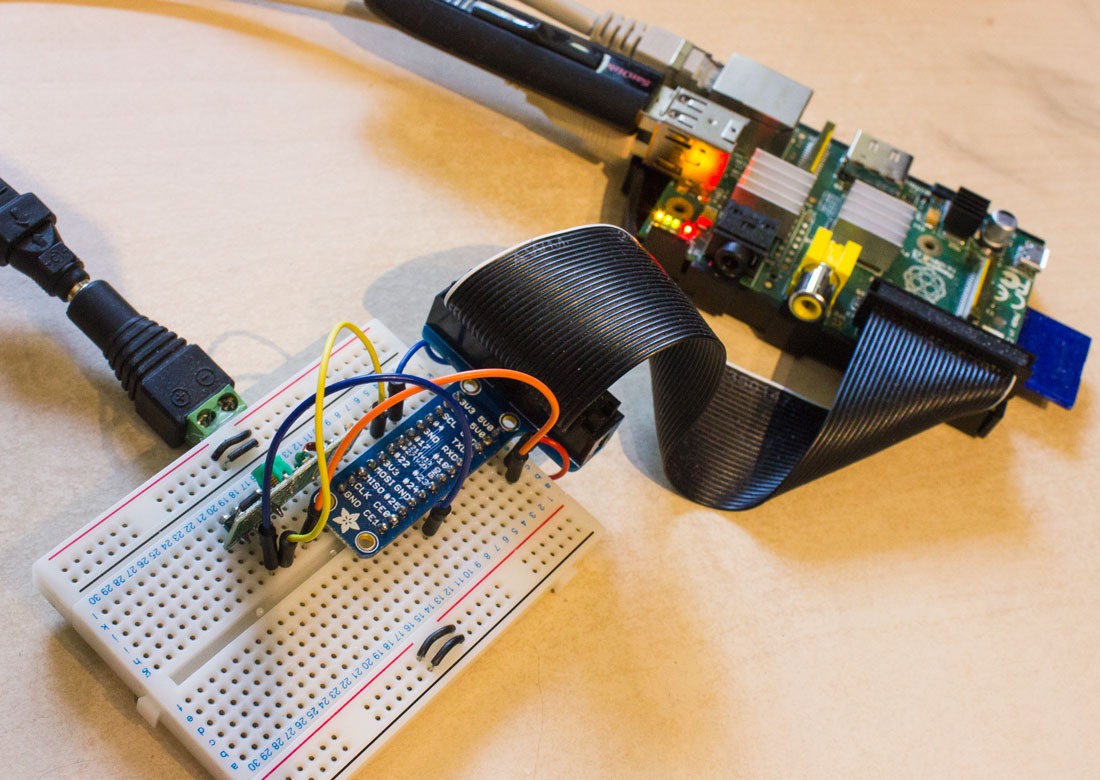
Decode 433 MHz signals w/ Raspberry Pi & 433 MHz Receiver PrinceTronics
This post will show you how to read 433 MHz codes using a Raspberry Pi. This tutorial was made to complement the Voice Controlling project which needed 433 MHz Unit Code Values to control the wireless switches. If you want to know how to read 433 MHz codes using an Arduino, go to this post!. I learned how to do this by reading this post.So credit goes to Paul Pinault for making this project a.

gpio How to decode a 433MHZ signal Raspberry Pi Stack Exchange
KC868-A4 smart controller, many hardware resources for you to use, you can write any code by Arduino IDE to ESP32 wifi/Bluetooth module. We will supply demo.

ESP8266 กับ 433MHz Receiver Part 1 Decode Signal YouTube
could you help me with code for Arduino to decode the sensor data. I have the same sensor as you but I would like to capture the sensor data with a 433mHz receiver and an Arduino Uno, write sensor data to serial. The receiver I have: 433Mhz RF Transmitter and Receiver Module Kit xy-mk-5v for Arduino Receiver module parameters 1.Product Model.

Decode and Send 433 MHz RF Signals with Arduino Arduino, Arduino radio, Arduino projects
Open the rc-switch "ReceiveDemo_Advanced" example sketch. Upload it and open the serial monitor. Hold your remote near your receiver module and press a button. The Arduino should decode the signal and print the results in the serial monitor. This is what I got for my remote-controlled mains switch when I press the button to turn channel 5 on:

Decode and Send 433 MHz RF Signals with Arduino Arduino, Decoding, Microcontrollers
The code we will be using to read the 433 MHz RF codes is actually located in the library as example code. To open up the code in the Arduino Software, press the "Open"-button, then press: libraries -> RCSwitch -> ReceiveDemo_Simple. Now the code should appear in the textfield. Now connect your Arduino to your computer and upload the code!

How 433MHz RF Module Works & Interfacing with Arduino
This guide shows you instructions to use somebody Arduino to decode 433 MHz signals from RF remotes, and send them with with Arduino toward remote-controlled controls some networking switches exit. Miss to content. Menu.. I subsequent the direction and everything uploaded fine, ME can even hear the transmitter send the signal (from get cheap.
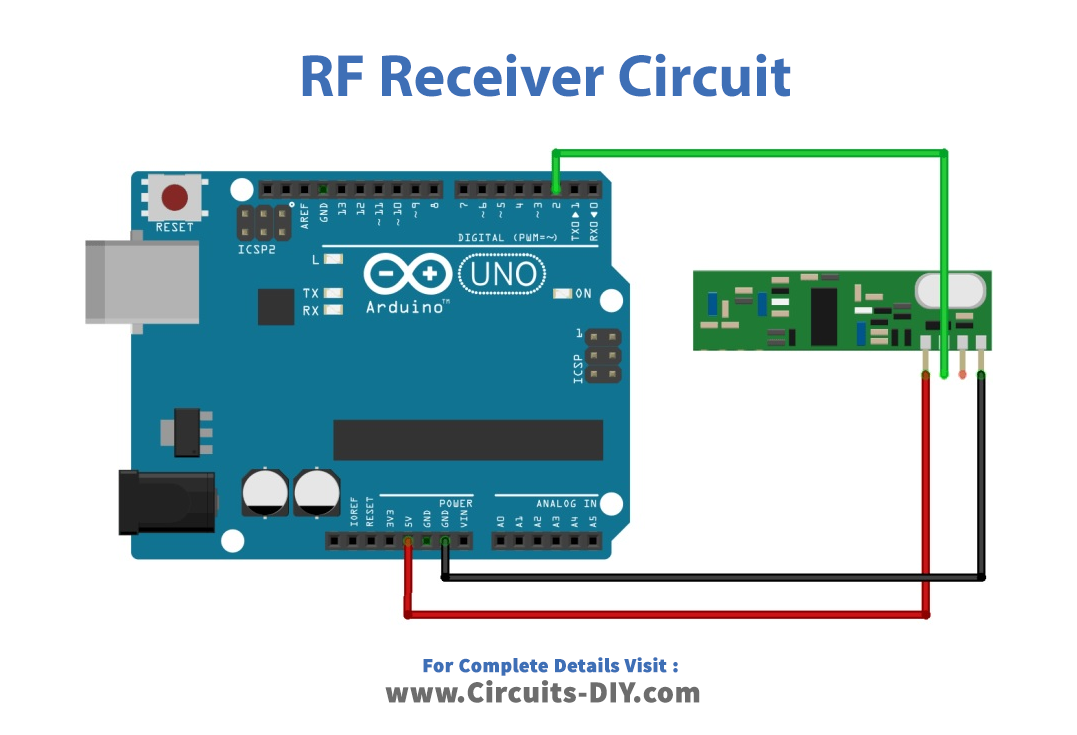
How to Decode and Send 433 MHz RF Signals with Arduino UNO
How to decode a 433MHZ signal. I've made the classic 433mhz send/receive experiment, using cheap hardware on the same breadboard and same raspberry, I've wired both sender and receiver to VCC 5V, GND to GND and data to GPIO 27 (receiver) and 17 (sender). I used the 433Utils as software and Piscope to check th result.

Decoding and Sending 433MHz RF Codes With Arduino and Rcswitch 9 Steps (with Pictures
So I started to decode manually all the signals applying the same protocol. The signal is a series of 12 tri-bits plus a sync-bit. For the Avidsen-like remotes there are 3 different tri-bit values (logically), they are called 0, 1 and F, for "floating".. "Decoding 433MHz RF data from wireless switches" was first posted on 28 February.
Decode 433 MHz signals w/ Arduino & 433 MHz Receiver PrinceTronics
Free Shipping Available. Buy 433mhz Decoder on ebay. Money Back Guarantee!

Decode and Send 433 MHz RF Signals with Arduino Random Nerd Tutorials
Working Explanation. To Decode and Send 433 MHz RF Signals with Arduino UNO, assemble the circuit according to the schematic. Now, first, you need to open the decoder sketch on IDE. So, for this purpose, go on files. Then go on examples. Go on RC_Switch, and open RecieveDemo_Advanced. Upload that particular code in Arduino.
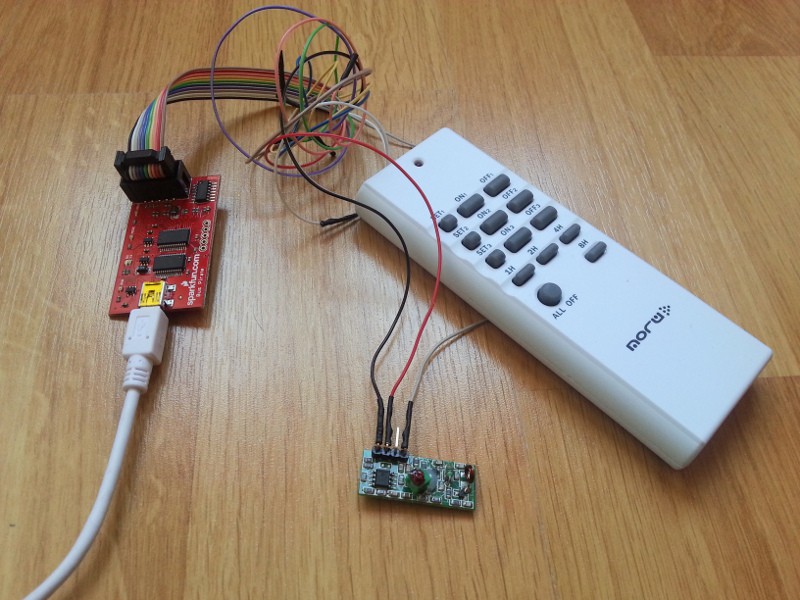

Decoding 433MHz RF Data From Wireless Switches Tinkerman
My analysis:-. Multiply the temperatures by 10 to create integers. 26.9 * 10 = 269 decimal = 100001101 binary. 43.8 * 10 = 438 decimal = 110110110 binary. A long distance between pulses is a 1, short distance is a 0. First 8 bits are the header or sync, next 16 bits are the temperature. The group of 8 close together pulses are the upper 7 bits.

Lesson31 How to decode 433MHz RF signal and control device by ESPHome YouTube
A soundcard makes for a very cheap oscilloscope. The focus of the tutorials is decoding the signals of a Nexa radio-controlled smart plug. [Joonas] first explores using an Arduino to do the job.

How to Decode and Send 433 MHz RF Signals with Arduino UNO
I have three 433mhz remotes that control various things in the house ( a light, a screen motor, and an awning) I tried to decode the signals from these remotes using a 433mhz receiver below: with the rc-switch library I can read the received signal /* Simple example for receiving GitHub - sui77/rc-switch: Arduino lib to operate 433/315Mhz devices like power outlet sockets. */ #include.